Understanding Pain Relief: The Role of Warm and Cold Compresses
Managing pain effectively is paramount for improving quality of life, whether one is dealing with chronic issues or acute injuries. Among various pain relief methods, warm and cold compresses stand out due to their simplicity, affordability, and immediate impact. Understanding the distinct roles these therapies play aids in making informed choices to manage discomfort better.
Understanding Pain Relief Methods
Historical Overview of Pain Relief Techniques
Pain management has evolved dramatically through the ages. Ancient civilizations relied on natural remedies such as herbal concoctions and hot springs. Egyptians used cold therapy by employing ice or cold water, while Greek physicians recommended warming up the body to alleviate pain. Over centuries, these rudimentary techniques have been refined into the modern warm and cold compress therapies we use today.
Modern Approaches to Pain Management
Today, pain management encompasses a broad range of techniques—including pharmacological interventions, physical therapies, and minimally invasive procedures. However, non-pharmacological methods like warm and cold compresses remain widely used due to their effectiveness and non-invasiveness. These therapies are frequently recommended by healthcare professionals as first-line treatments before considering more aggressive measures.
Benefits of Warm Compresses
Mechanism of Action
How Heat Therapy Works on the Body
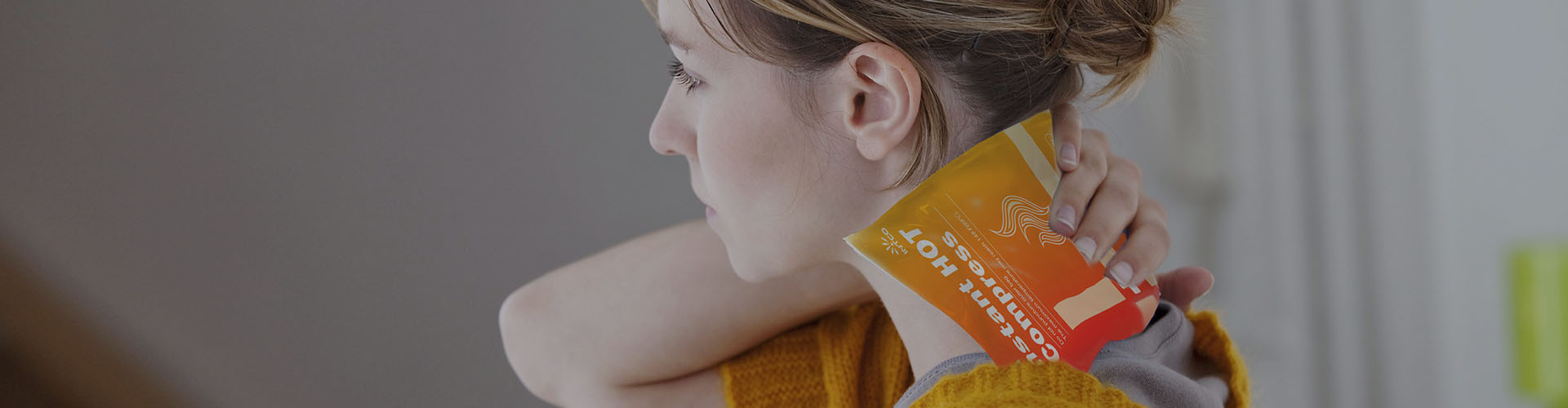
When applied to the body, heat therapy—via warm compresses—increases the temperature of the targeted area. This elevated temperature facilitates muscle relaxation, reduces stiffness, and improves flexibility. The warmth acts by dilating blood vessels, which promotes enhanced blood flow, delivering more oxygen and nutrients to the area while aiding in the removal of waste products.
Improving Blood Circulation
Warm compresses significantly improve blood circulation in the applied area. As blood vessels expand, more blood is transported, helping to soothe muscles, repair tissues, and speed up the healing process. This increased circulation not only helps alleviate pain but also reduces muscle stiffness and encourages quicker recovery from injury.
Specific Conditions Benefiting from Warm Compresses
Muscle Stiffness and Spasms
Warm compresses prove highly effective in treating muscle stiffness and spasms. By increasing the blood flow to the affected muscles, heat helps to relax contracted muscles, reducing pain and enhancing mobility. This makes warm compresses an excellent treatment option for individuals suffering from chronic muscle pain or those recovering from intense physical activity.
Arthritis and Joint Pain
Individuals with arthritis or joint pain often find significant relief through the use of warm compresses. The heat from the compress helps to ease stiffness in the joints and improve flexibility, making daily activities less painful and more manageable. By aiding in the reduction of joint inflammation and promoting blood flow, warm compresses serve as a valuable tool for managing arthritis symptoms effectively.
Benefits of Cold Compresses
Mechanism of Action
How Cold Therapy Works on the Body
Cold therapy, or cryotherapy, reduces the temperature of the targeted area when applied. This decrease in temperature causes blood vessels to constrict, which slows down blood flow and reduces swelling. Additionally, cold therapy numbs the area, providing pain relief by decreasing nerve activity. This dual mechanism of reducing inflammation and numbing makes cold compresses particularly effective for acute injuries.
Reducing Inflammation and Numbing Nerve Endings
Cold compresses excel in reducing inflammation and numbing nerve endings. By constricting blood vessels, they limit the flow of blood to the area, curbing swelling and inflammation. The cold acts almost like an anesthetic, numbing the affected area and minimizing pain by disrupting the transmission of pain signals to the brain. This approach is particularly useful in managing injuries that result in immediate swelling and intense pain.
Specific Conditions Benefiting from Cold Compresses
Acute Injuries and Swelling
Cold compresses are highly effective for treating acute injuries and swelling. Applying cold to a fresh injury slows down bleeding by constricting blood vessels and reduces swelling by limiting fluid buildup. This makes cold compresses an ideal first response to sprains, strains, and bruises. Their ability to minimize inflammation and alleviate pain rapidly makes them an essential component of injury management.
Migraine Relief
For those suffering from migraines, cold compresses can offer rapid relief. The numbing effect of the cold can alleviate the intense pain and discomfort associated with migraine headaches. Applying a cold compress to the forehead or the back of the neck can help reduce migraine symptoms by diminishing the throbbing pain and providing a soothing, cooling sensation that helps relax the muscles and blood vessels involved.
Choosing Between Warm and Cold Compresses
Factors to Consider
Type of Injury or Condition
Choosing between a warm or cold compress often depends on the type of injury or condition being treated. Acute injuries, such as sprains or strains, typically benefit more from cold compresses due to their ability to reduce swelling and numb pain. Chronic conditions, like arthritis or muscle stiffness, are better managed with warm compresses as they help improve blood flow and relax muscles. Identifying whether the pain is due to inflammation or muscular issues is crucial in making the right choice.
Timing and Duration for Each Method
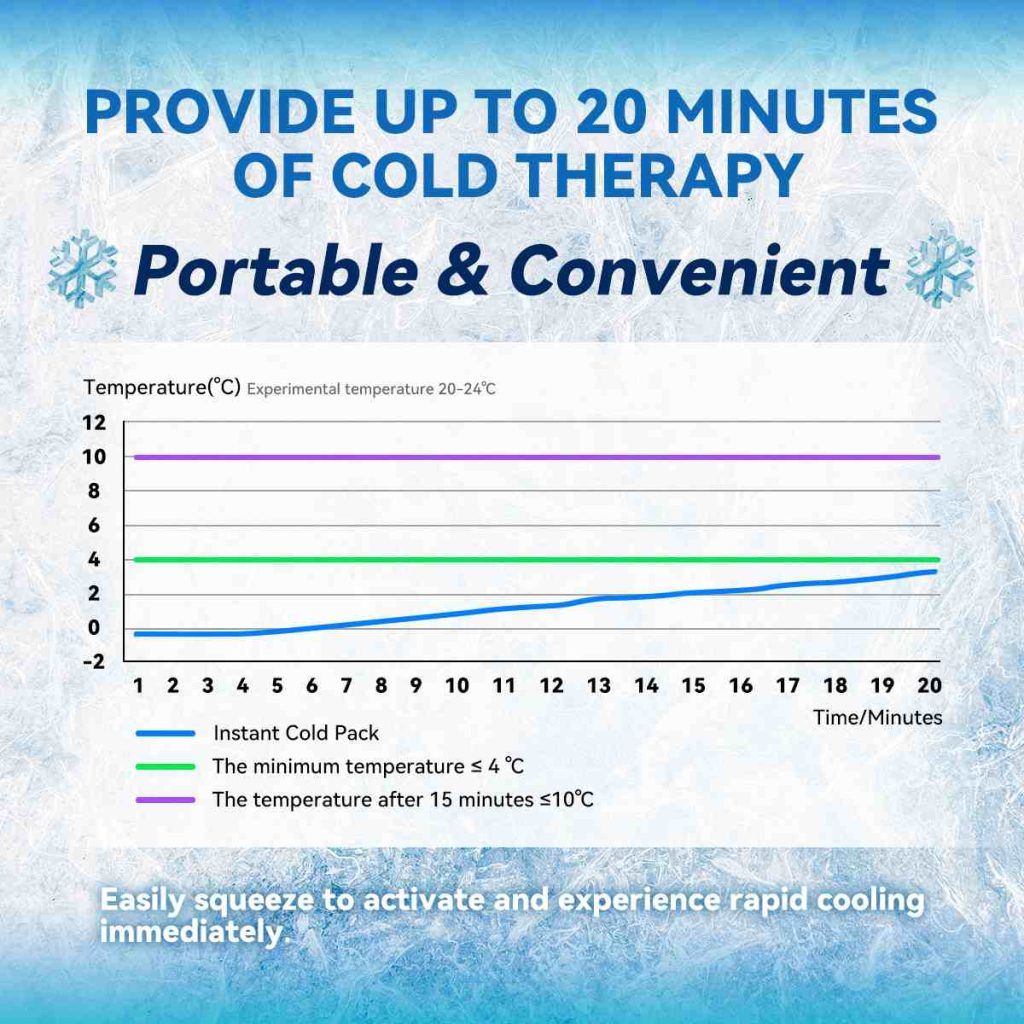
Timing and duration are vital when deciding between warm and cold compresses. Cold compresses are most effective when applied within the first 24 to 48 hours of an injury to reduce inflammation and numb the area. They should be used in intervals of 15-20 minutes with breaks in between to prevent frostbite. On the other hand, warm compresses are best used after the initial inflammatory phase has passed or for chronic conditions. They can be applied for 15-30 minute intervals to enhance blood flow and ease stiffness.
Application Techniques for Optimal Results
Best Practices for Warm Compress Application
Types of Warm Compresses Available
Various types of warm compresses are available, including electric heating pads, microwavable heat packs, and warm water bottles. Each type has its advantages and can be selected based on personal preference and the area needing treatment. Electric heating pads provide adjustable heat with continuous warmth, while microwavable heat packs are portable and convenient for on-the-go use. Warm water bottles are a traditional, cost-effective option that also offers customizable warmth.
Safety Precautions to Follow
While using warm compresses, certain safety precautions should be observed. Always check the temperature before application to avoid burns. Use a cloth or towel as a barrier between the compress and the skin. Limit application time to avoid overheating the area, and never use heat on an open wound or infection as it can exacerbate the condition. It’s also important to consult healthcare providers, especially if you have conditions like diabetes or nerve disorders, which can affect temperature sensation.
Best Practices for Cold Compress Application
Types of Cold Compresses Available
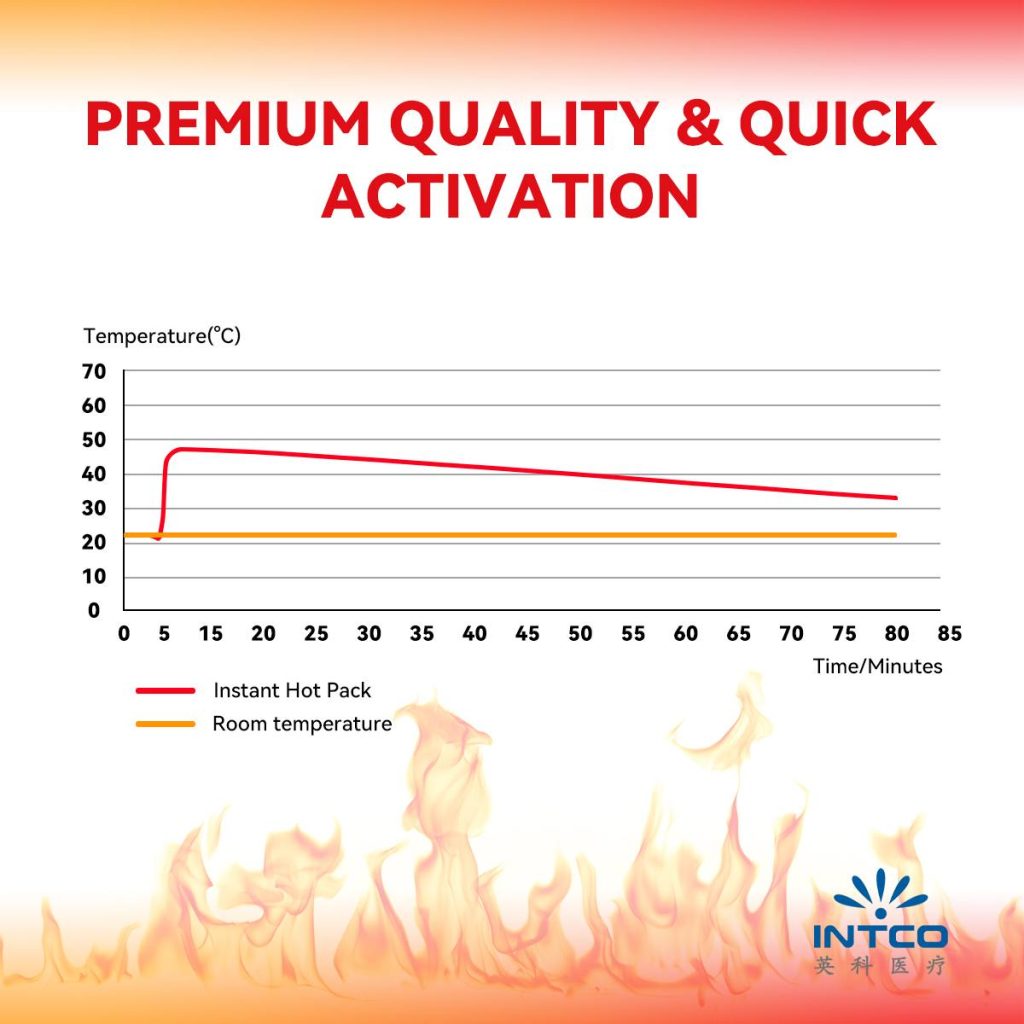
Cold compresses come in various forms, such as reusable gel packs, ice bags, and instant cold packs. Reusable gel packs are flexible and can be easily molded around joints and other body parts. Ice bags, filled with crushed ice or cubes, provide a traditional and effective cooling method. Instant cold packs are convenient for emergency use and produce cold when a chemical reaction is activated, making them ideal for first-aid kits and active lifestyles.
Safety Precautions to Follow
Applying cold compresses also requires adherence to safety measures. Always place a cloth or towel between the cold compress and the skin to prevent frostbite. Limit the application to 15-20 minute intervals, with breaks in between, to avoid skin damage. Avoid using cold therapy on individuals with circulatory issues, as the reduced blood flow can exacerbate these conditions. Consulting healthcare providers is advisable for those with pre-existing health concerns to ensure safe use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Common Queries About Warm Compress Usage
Many individuals have questions regarding the use of warm compresses. One common query is how often warm compresses should be applied. It’s generally recommended to use them in intervals of 15-30 minutes, 2-3 times daily, depending on the condition being treated. Another question is what materials can be used for warm compresses; options include heating pads, warm towels, and microwavable heat packs. Additionally, people often ask if warm compresses can be used for eye conditions—yes, they are effective for managing conditions like styes and dry eyes. Safety concerns are also common, with individuals wondering how to avoid burns—utilizing cloth barriers and testing the temperature beforehand are key practices.
Common Queries About Cold Compress Usage
Similarly, there are frequent questions about cold compresses. One significant question is how long to apply cold compresses. They should be used in 15-20 minute intervals with breaks to prevent skin damage. Users often ask what the best circumstances for cold compress application are; ideal scenarios include acute injuries, inflammation, and swelling. Another recurring question is whether cold compresses can be used for headaches, and indeed, they can be highly effective for migraines and tension headaches. Lastly, queries about safety measure highlight the importance of using a barrier, avoiding prolonged exposure, and consulting healthcare providers for proper guidance.
In conclusion, warm and cold compresses offer distinct benefits and serve as effective, non-invasive methods for pain relief. By understanding their mechanisms, applications, and safety precautions, individuals can effectively use these therapies to manage various types of pain and improve their quality of life. Consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice ensures optimal results and safe usage, empowering individuals to take control of their pain management strategies sustainably.
Whether it is warm compresses or cold compresses, INTCO can provide you with excellent products INTCO Healthcare offers a range of cold and hot packs to provide relief for various ailments. The Hot & Cold Gel Pack is a versatile product that can be used for both cold and hot therapy. Cold therapy is effective in reducing swelling and pain caused by inflammation, making it suitable for joint and muscle injuries, back and neck pain, arthritis, sinus and stress headaches, post-surgical pain, sunburn, and other burns. On the other hand, heat therapy provides physical warming for the skin, improving blood circulation and helping to relax tight muscles. It is beneficial for muscle pain and soreness, muscle spasms and cramps, arthritis, menstrual cramps, and chronic neck or back stiffness. The gel packs come in different sizes and colors to cater to individual needs.